Insight into Forest Management
Staatsbosbeheer, forest management and forest strategy
The image that has emerged in recent years that Staatsbosbeheer, the Dutch forestry commission, is felling trees on an industrial scale throughout the country is incorrect. An audit by the Netherlands Court of Audit shows that Staatsbosbeheer does not fell trees faster than they grow. However, it is not known whether the working methods of the Netherlands’ largest forest manager and other forest owners are delivering the desired long-term results.
We have audited Staatsbosbeheer’s strategy and a number of goals the government set in its national forest strategy.
Forest managers have to make informed decisions if they are to achieve the various sustainable forest management goals. Staatsbosbeheer’s goals are to promote recreation, optimise the use of forests and protect biodiversity. But it does not know what impact all the local and regional forest management decisions have or how much maintenance is overdue. As a result, neither does the Minister for Nature and Nitrogen Policy. The Court of Audit concludes in a report entitled Insight into Forest Management, published on 6 December 2022, that the minister and the provinces — Staatsbosbeheer’s main funding source — do not collect enough information to adapt or properly monitor forest management policy.
Nationally 10% more forest probably unrealistic
Current regulations and their implementation do not guarantee that forests will be managed sustainably. Nationally, for instance, there is insufficient replanting of forests. Not all provinces actively monitor the replanting obligation. Heavily forested provinces such as Gelderland, North Brabant and Drenthe are satisfied with Staatsbosbeheer’s forest maintenance. However, the goals of the individual provinces vary and do not always match those in the national forest strategy.
The various administrative tiers involved in forest management have not yet made agreements on who will pay for the planting of new trees. Staatsbosbeheer will probably be able to plant an additional 5,000 hectares of forest on its own land in the coming years. The rural forest strategy, signed jointly by the government and the provinces in 2020, requires 10% more forest in the long term. That objective is unlikely to be achieved. Since 2013, more trees have been felled in the Netherlands than planted by all nature managers. There is more than 6,000 ha less woodland than assumed at the start of the Woodlands Strategy.
Staatsbosbeheer’s wood harvest
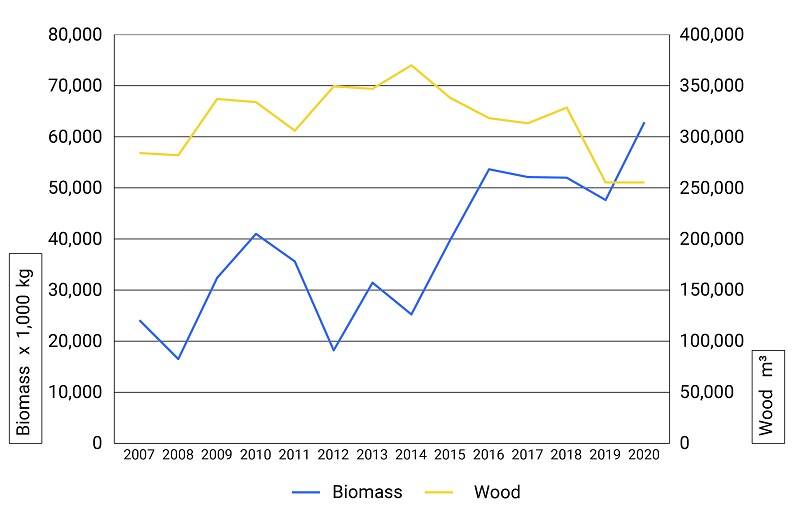
Further decline in wood harvest
Staatsbosbeheer’s is harvesting less wood than in the past. This is due in part to drought and the mass die-back of ash and spruce trees in recent years. The harvest is expected to decline by a third in the years ahead. Staatsbosbeheer is not felling more trees to generate more income. Financial circumstances are also reducing the volume of logging. The profit on the sale of wood has been declining since 2015. An increase in wood harvesting is one of the national goals.
Provinces
Responsibility for nature and landscape was largely decentralised to the provinces in 2014. Last year they granted Staatsbosbeheer €69 million for landscape management. The national contribution from the Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality (LNV) is much lower: last year just over €28 million (8.2% of Staatsbosbeheer’s total income). LNV also pays for nature restoration projects. As a green utility company, Staatsbosbeheer generates most of its income comes from the sale of wood and biomass, the provision of recreational services and the leasing out of land. In total, it manages 270,000 hectares, of which about 35% is forest.
In view of the allocation of tasks and responsibilities, there must be a common understanding of the results of nature and forest management.
What are our recommendations?
We recommend that the Minister for Nature and Nitrogen Policy reach agreement with Staatsbosbeheer on the information she needs to oversee the effects of policy. Further agreements are also needed with the provinces. Agreements with both the provinces and large forest managers should explain how the national targets can be achieved.
Why did we audit forest management?
Our audit was designed to increase certainty about the sustainability of Staatsbosbeheer’s forest management. Staatsbosbeheer is an autonomous administrative authority. The audit also considered the state of two of the rural forest strategy’s goals: 10% more forest by 2030 and a slight increase in the amount of wood harvested.
What audit methods did we use?
We collected information on Staatsbosbeheer’s income and expenditure, on logging, the laws and regulations applying to sustainable forest management and related agreements. We also conducted interviews, carried out fieldwork in 3 provinces and analysed documents. Data on logging were requested from Staatsbosbeheer.
Current status
The Minister for Nature and Nitrogen Policy and Staatsbosbeheer have responded to our audit findings. The report was presented to parliament on 6 December 2022 and made public on the Court of Audit’s website.